Distributed Wind Energy
What Is Distributed Wind Energy?
Wind turbines that serve on-site energy demand or support local electricity networks produce what is known as “distributed wind energy.” This is in contrast to large-scale wind power plants either on land or offshore that supply bulk power to the electric grid across much larger service territories.
The distributed wind energy market includes wind turbines and projects of many sizes, from small wind turbines powering remote telecommunications equipment (which provide less than 1 kilowatt of power) to multimegawatt wind turbines that power campuses or large factories.
Distributed wind turbines can provide all the power used at a location, or they can provide part of the power to offset utility bills. In some instances, extra power produced by a community or residential wind energy project can be sold to utilities companies or other nearby energy users.
Explore the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Wind Energy Technologies Office (WETO) 10 things you may not have known about distributed wind energy and the Distributed Wind Energy Resource Hub, which helps anyone interested in harnessing the power of distributed wind energy with a curated directory of basic information, project funding and technical assistance, case studies and success stories, and tools to evaluate your location's potential.

Distributed wind turbines, like this Bergey Excel 15, can help provide electricity to buildings, local grids, and small communities. Photo from Nelson Aerial Productions
How Can Distributed Wind Energy Help Meet Energy Goals?
Distributed wind energy helps provide on-site electrical power that can lower energy costs, benefits local environments, focuses on local-level needs and considerations, creates local jobs, supports domestic supply chains, and provides economic opportunities for communities and residences.
DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory has published an analysis of the U.S. distributed wind market on behalf of WETO indicating that there is more distributed wind energy that could be profitably deployed today across the United States than has been deployed worldwide so far.
The United States has significant potential for distributed wind energy. According to DOE’s 2023 Distributed Wind Market Report, the cumulative U.S. distributed wind capacity installed from 2003 through 2022 was 1,104 megawatts (MW) from over 90,000 wind turbines across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, the Northern Mariana Islands, and Guam.
DOE, in partnership with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and certification bodies such as the Small Wind Certification Council, works to increase the number of certified small and medium wind turbines on the market and increase consumer confidence in their performance. With support from WETO, national labs are also conducting research to improve site assessment methods for distributed wind turbines and help advance distributed wind technology innovation.
Check out interactive animations of how distributed wind energy works, how wind turbines work, and how distributed wind could support your electricity needs in a 3D virtual model—or read more below.
Distributed Wind Energy Applications
There are many ways that wind can support distributed energy markets. Review case studies and an interactive three-dimensional animation on WETO’s website, which includes wind energy that can offset electricity costs, improve energy independence and resilience, and/or provide on-site power for:
- Isolated and remote communities , like rural Alaska or island villages that are off grid, including homes, businesses, and community buildings
- Residential settings, in individual homes and smaller microgrids, sometimes integrated with other distributed energy technologies, such as solar panels and battery storage
- Public facilities and services, such as water treatment plants
- Agricultural sites, such as farms
- Commercial buildings and electric vehicle charging stations
- Industrial parks
- Mobile, pop-up deployment in military or disaster-relief scenarios.
Agricultural and residential customers made up 59% of all U.S. distributed wind projects in 2022. These applications have great potential, especially if combined with other distributed energy technologies, such as solar photovoltaics and energy storage. In many cases distributed wind can also be used to provide expanded energy resilience or reliability for important energy needs, such as emergency services.
Learn more about just a few places U.S. energy consumers are using distributed wind energy, ranging from a remote village. There are many benefits to community wind energy projects, though they are also subject to regulations and zoning restrictions.<
Read more about community and residential wind energy below.
Community Wind Energy
What Is Community Wind Energy?
The term “community wind energy” describes wind energy projects that have been built for the benefit of local community members. Community members may own these projects directly, through an intermediary (such as a municipal government or rural electric cooperative), or benefit from the project as subscribers, paying a private owner for a share of the project’s output. The term can describe small-scale distributed wind energy projects, in which wind turbines generate power at or near the site or sites where the power is consumed, such as at a school, or larger projects that include several-megawatt-sized wind turbines.
At first glance, some community wind projects may resemble smaller, standard, land-based, utility-scale wind power plants. However, where they differ is in who primarily receives the energy and other benefits generated by the project. Community wind projects deliver electricity to local community facilities or may be shared by many people in the community.
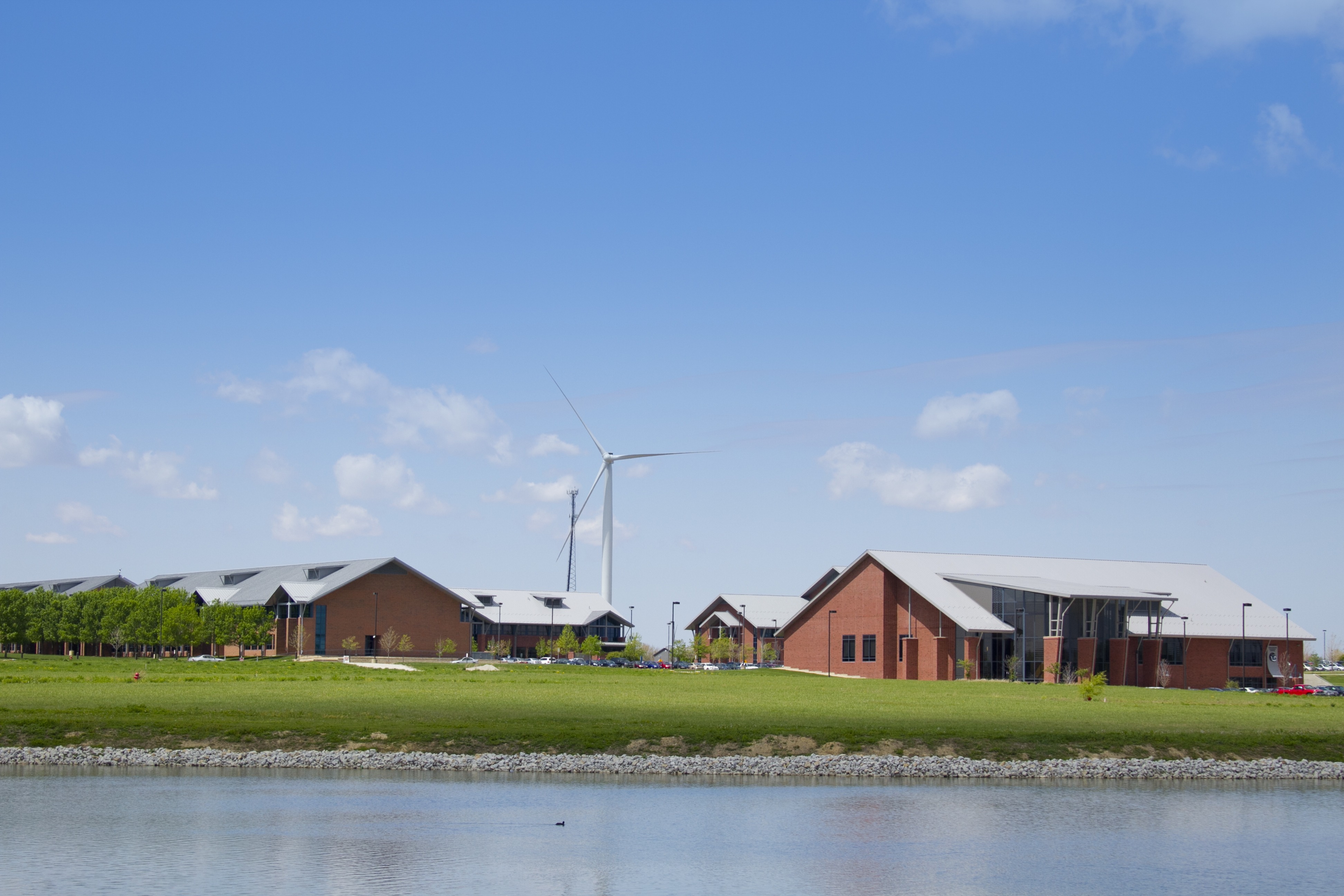

Located in Normal, Illinois, Heartland Community College uses electricity from a 1.65-megawatt wind turbine to meet its own energy needs. Photo from Harvest the Wind Network
How Are Community Wind Energy Projects Used?
Community wind energy projects have many applications:
- Schools, hospitals, businesses, farms, ranches, or community facilities can use a locally owned wind energy project to supply their electricity.
- Rural, isolated, or islanded electric cooperatives or municipal utilities can develop their own community wind projects to diversify electricity supplies.
- Government, industrial, or commercial facilities can supplement their energy supplies, improve energy resilience, and offset utility costs.
- Local individuals can also form independent power producer groups or limited liability corporations to sell the power the turbines produce to a local electricity supplier.
What Are the Benefits of Community Wind Energy?
Although many distributed wind projects may have similar benefits, community wind energy has many benefits for the community it serves and beyond.
Energy
The electricity generated by wind energy does not pollute the water we drink or the air we breathe, so wind energy means less smog, less acid rain, and fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Wind energy reduces health care and environmental costs associated with air pollution. Finally, wind energy does not require mining, drilling, or transportation of fuel, meaning it poses few environmental risks to the areas where wind energy projects are located.
The electricity generated by wind energy does not pollute the water we drink or the air we breathe. Wind energy reduces health care and environmental costs associated with air pollution. Finally, wind energy does not require mining, drilling, or transportation of fuel, meaning it poses few environmental risks to the areas where wind energy projects are located.
Local Control
Because many community wind energy projects are locally owned, residents can have more influence over the siting and sizing of projects and ensure that the projects honor local concerns related to issues such as setbacks from homes and businesses, sound levels, and viewshed impacts.
Stable Energy Prices
Wind energy projects do not require fuel to operate, and their overall operating costs are relatively low. This means owners of community wind projects can confidently predict the price that they will pay for energy throughout the lifetime of the project.
In addition, community wind projects produce energy that can be used directly or sold to local utilities at a fixed rate through a power purchase agreement, providing stable long-term energy prices. Finally, in areas where importing fuel results in high electricity costs, community owned wind projects provide locally produced power, which can stabilize or lower energy costs. As communities consider the expanded use of electric vehicles for public services, such as electric school buses, having a more convenient long-term energy option with minimal cost variation will benefit most communities.
Job Creation
Wind energy—whether community or privately owned—often brings a [range of new jobs](https://windexchange.energy.gov/training) to the area where a wind project is sited. This can include short-term jobs, like those in construction, as well as long-term roles operating and maintaining the wind project.
Wind energy development can also drive an [increase in jobs](https://windexchange.energy.gov/economic-development-guide) not directly related to the wind project. For example, the construction phase of a large wind farm may bring in workers from out of town, meaning hotels and restaurants need to increase their staff to accommodate the influx of potential patrons.
Residential Wind Energy
What Is Residential Wind Energy?
Residential wind energy is generated at the source of consumption. In other words, it is wind energy generated at and connected to the residence it powers. Small wind projects can be as simple as a single wind turbine on private property. These same principles would also apply to small business, such as farms or other agricultural businesses, or even small industries located outside of communities across the nation.
A residential wind energy system can be just one turbine or a group of turbines with each turbine ranging in size from 200 watts—enough to charge a battery for a recreational vehicle—to tens of kilowatts to power larger residences or small farms.
Residential distributed wind energy allows landowners to harness the energy created by wind and use as much as they need to power their home and other buildings on their property. A landowner can connect their distributed wind turbine to the grid, or the energy can stay off the grid in standalone applications.
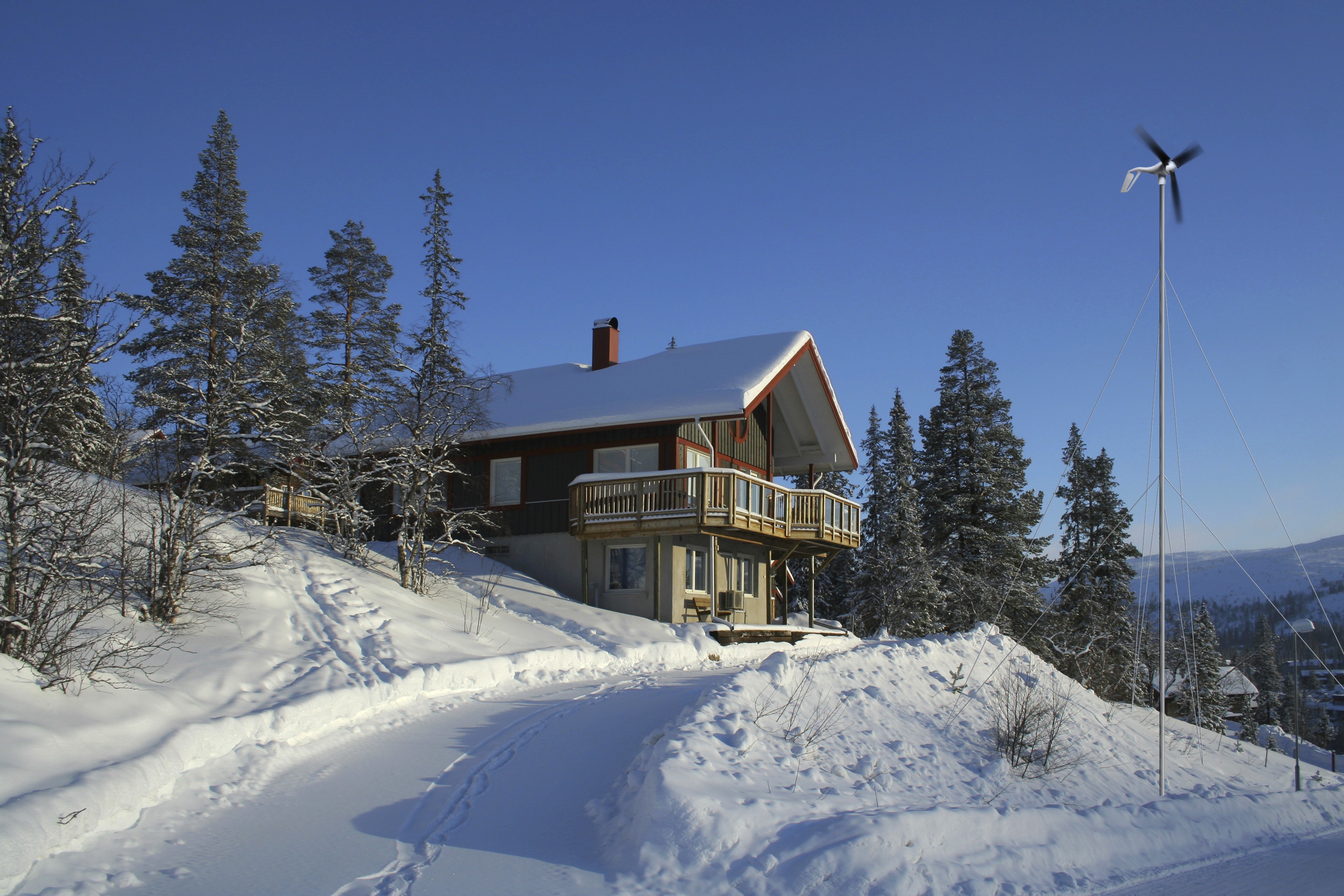

Residential wind energy can help provide electricity to remote homes. Photo from Ketter Ulrich, Primus WindPower
How Are Residential Wind Energy Projects Used?
Homeowners use residential wind energy, which can offset a homeowner’s electricity costs, to power their homes and sometimes even recreational vehicles and boats.
In some cases, a residential wind energy system is paired with other sources of distributed energy, such as solar panels, energy storage, or fossil fuel generators, in a home-scale microgrid. This type of system can help homeowners meet all their energy needs using power generated on their property.
When the residence is connected to the distribution network, a residential wind energy system can supplement a home’s energy consumption. If the residential distributed energy system provides more electricity than is used, the residence may be “net-zero” although it still uses energy from the grid when there is not enough wind for the wind turbine. If combined with other energy sources as part of a home microgrid, the residence can be self-sustaining and can operate without a grid connection, either permanently, which is known as being “off-grid systems”, or if the grid goes down during a weather event or other emergency situation.
How a wind turbine connects to the local grid is driven largely by local building codes and rules put in place by the local utility, typically driven by state “net-metering” laws.
What Are the Benefits of Residential Wind Energy?
Residential wind can help homeowners:
- Lower their electricity bills
- Allow individuals or businesses to consume more energy than is available from their local utility
- Avoid the high costs of having utility power lines extended to a remote location
- Improve homeowners’ resilience during extended utility outages or support local grid conditions at the end of long distribution feeders.
- Generate on-site power in rural areas.
According to the 2020 U.S. Census, approximately 20% of the U.S. population lives in rural areas. Rural residences are better suited for distributed wind, given greater land availability, lack of local obstructions in the form of tall buildings, and in many parts of the country, stronger winds.
How Do I Install Distributed Wind Energy in My Area?
To find out if distributed wind power is a good option for you, start by learning the basics of owning, hosting, or partnering with wind power.
If you’re interested in constructing a wind project, check out the following WINDExchange guidebooks and handbooks:
- The Distributed Wind Energy Resource Hub, which helps anyone interested in harnessing the power of distributed wind energy with a curated directory of basic information, project funding and technical assistance, case studies and success stories, and tools to evaluate your location's potential.
- The National Distributed Wind Network, which helps people considering using distributed wind energy technologies for onsite and local power needs to support businesses, homes, farms, and communities with fact-based resources, support for your project, and in-person and virtual events.
- The Small Wind Guidebook, which helps homeowners learn more about distributed wind and whether installing a small wind turbine might be a good investment. The guidebook includes FAQs, wind resource maps, and a description of the steps to install distributed wind.
- The Small Community Wind Handbook, which was designed to provide guidance for a community to install a small wind power project to provide electricity for their needs.
- The Large Community Wind Handbook, which helps communities decide whether to and how to install a larger distributed wind energy project for their benefit and potentially beyond.
- Although not related to distributed wind energy, the Community Benefits Guide, which outlines benefits communities might receive from developers of utility-scale land-based or offshore wind energy in their ariea.
Additionally, learn more about wind energy ordinances on the federal, state, and local levels, which govern many aspects of wind energy development.